Stores
If you want to see the API specs, click here.
Stores are a central entity in workflow. You can use them to collect data, to modify records in existing workflows via lookup mappings, and you can use them to send data to other applications. We'll dive into greater detail in this section.
Store options
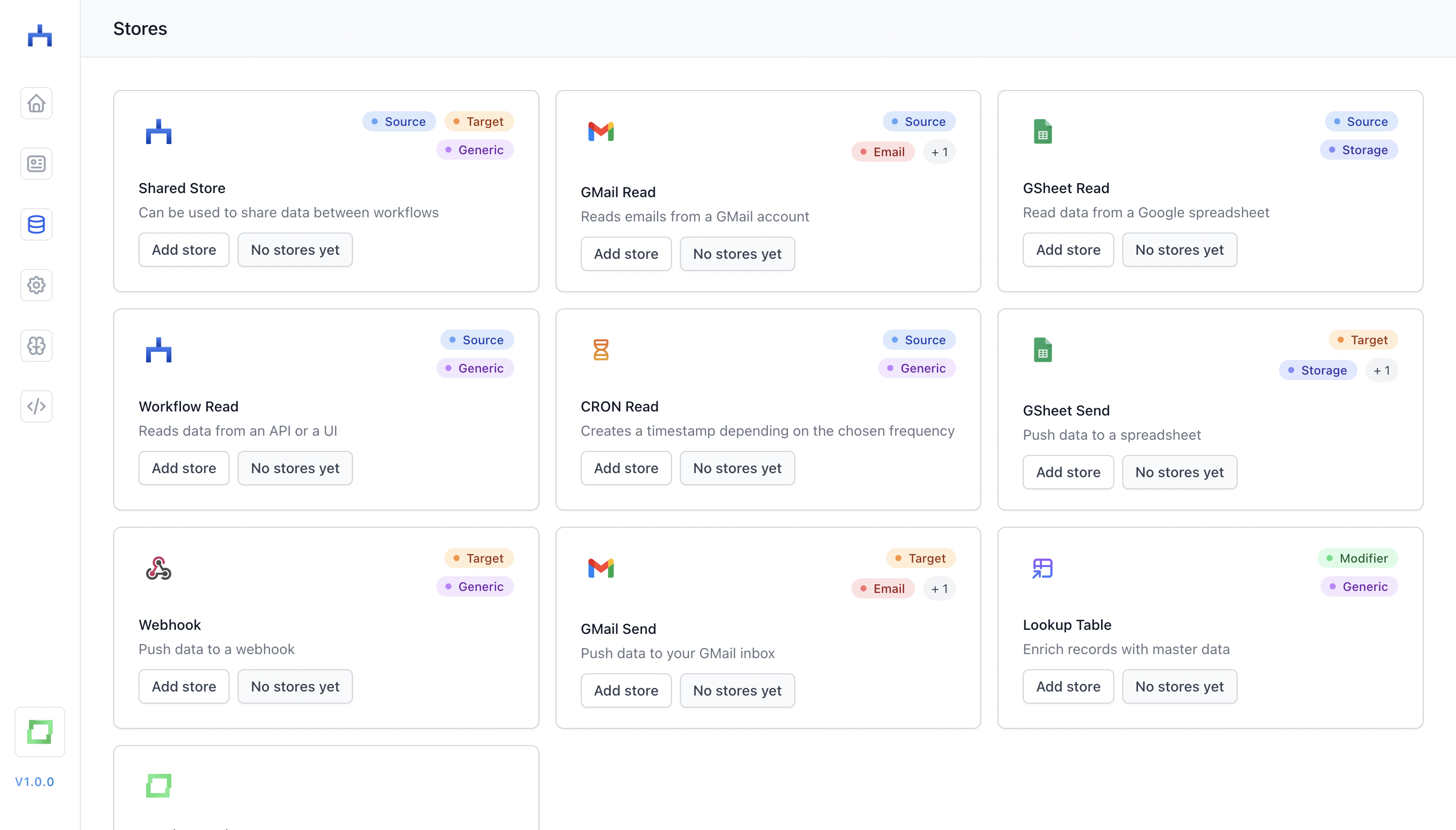
A store belongs to at minimum one of these three categories:
sources: you're collecting data. That could be e.g. a Google spreadsheet you want to process, or the Workflow API which you can post data to.targets: you're sending data to other applications. A target store contains the logic to process incoming records with the integration-specific logic, i.e. pushing data to the "GMail Send" store will categorize your inbox, or it will create drafts for you.modifiers: use them as a step in your workflow to enrich records via lookup tables.
You can see all existing store options in the store catalogue:
Adding stores
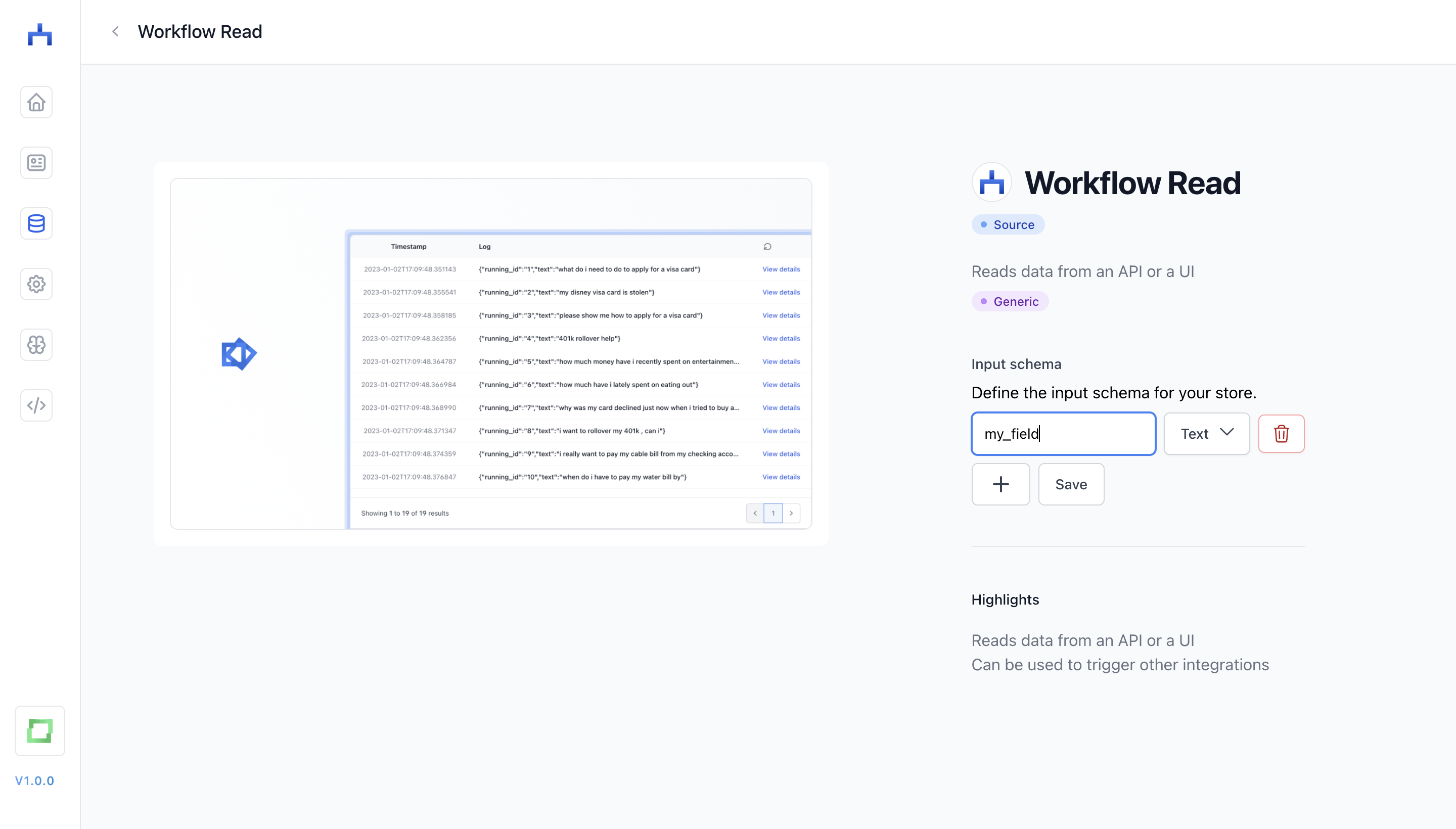
Each store has its own logic to be added; generally, you can click on Add store if you want to add one. The logic to add a store ranges from authenticating Google via Oauth up to creating a schema. In our example here, we create a "Workflow Read" store by defining which fields we'd like to have in the store:
Maintaining stores
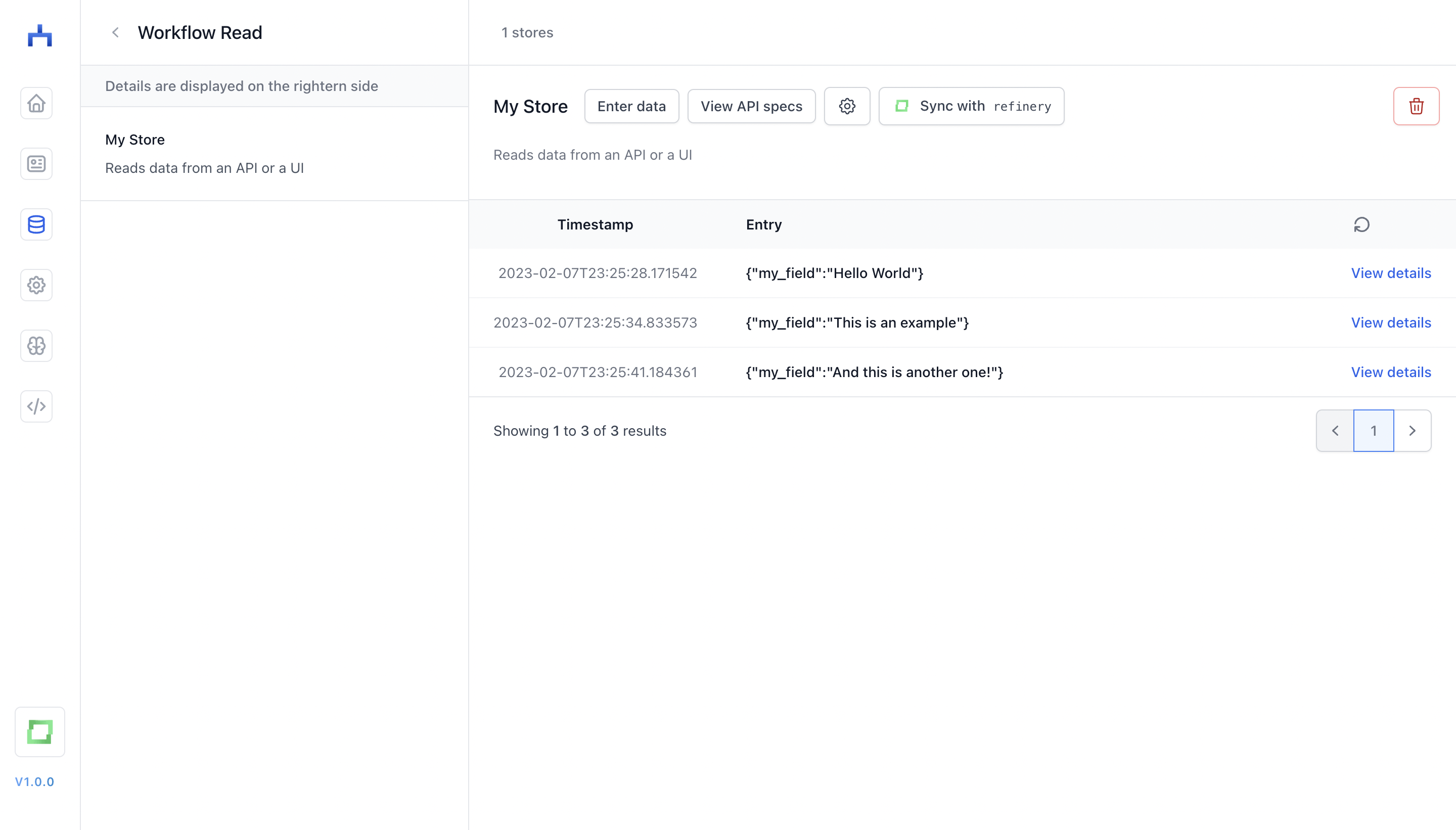
For every store, you can look into the current entries:
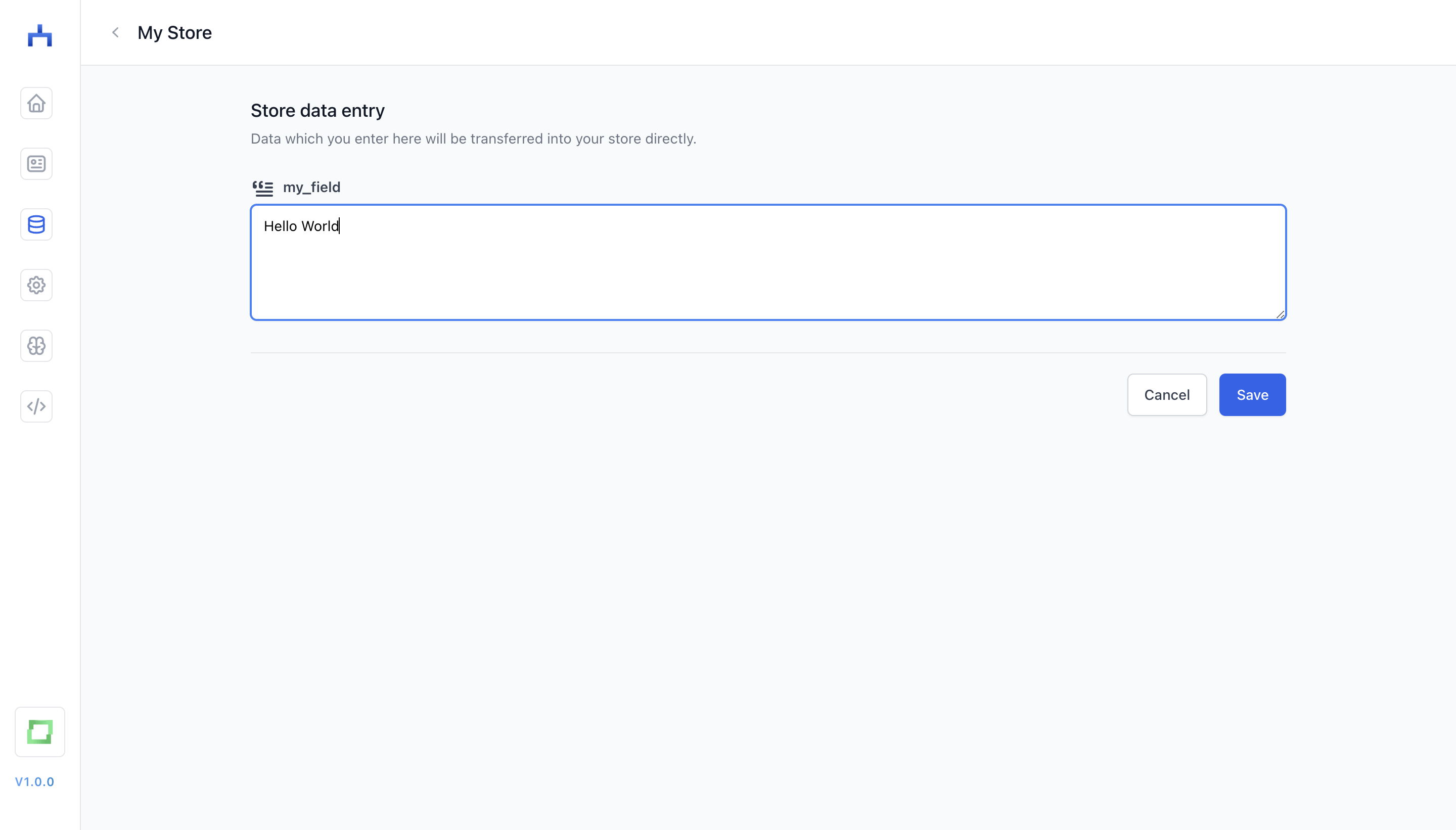
In some cases, you can enter data manually:
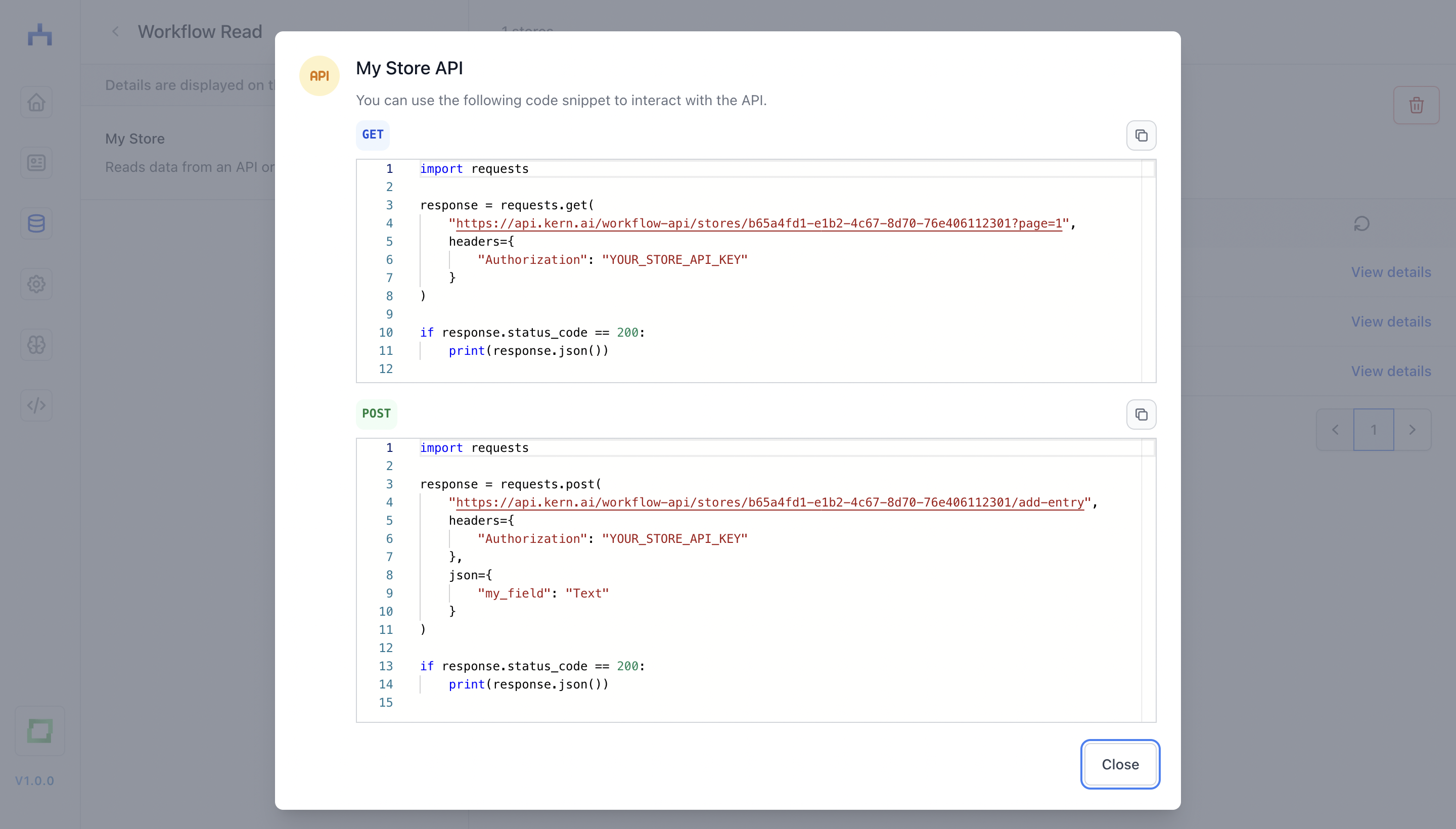
What options you have in a store is highly depending on the integration used to build that store. For the "Workflow Read" store, you can also post data to the store via API (see also below):
Synchronizing a store with refinery
One of the key benefits of using workflow is that you can synchronize stores with refinery. For instance, if you have an inbox you want to use to steadily grow your database, you can simply set up a refinery project from the store itself.
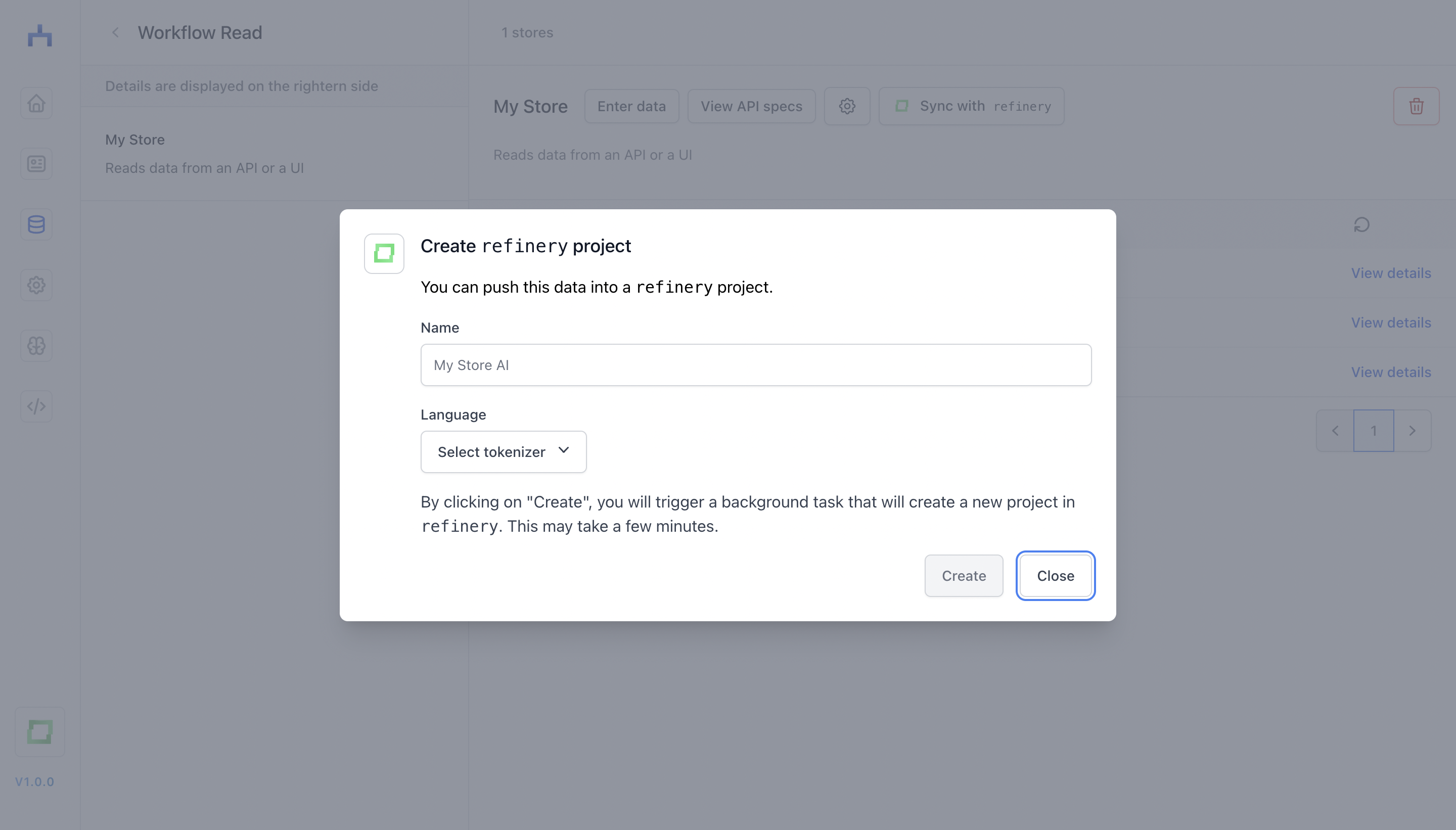
Once you set up a synchronization, a batch job will be started to push the current store data to a newly created refinery project. Afterwards, new incoming data is directly sent to the refinery project and appended to the database.
Store API
You can easily retrieve stores from workflow via their unique ID and an access token you create in the application. This is helpful if you want to monitor the size of your stores programmatically, or if you want to add new entries to the API.
The store model
The store model contains informations such as the name, integration, and the entries.
Properties
- Name
id- Type
- string
- Description
Unique identifier for the store.
- Name
organizationId- Type
- string
- Description
Unique identifier of the organization in which the store exists.
- Name
name- Type
- string
- Description
The name of the store itself.
- Name
integration- Type
- string
- Description
The name of the integration via which you created the store (from the store catalogue).
- Name
icon- Type
- string
- Description
The unique name of the icon to display the store.
- Name
configSetup- Type
- dict
- Description
The configuration you provided during the initiation of the store.
- Name
configActions- Type
- dict
- Description
If this is a store which triggers specific configurable actions, this dictionary will contain the information what to do (e.g. draft messages for the GMail Send store).
- Name
refineryProjectId- Type
- string
- Description
If this store is synchronized with a project in refinery, it will contain its unique identifier.
- Name
entries- Type
- list[store-entry]
- Description
Contains N entries of your store.
- Name
numEntries- Type
- int
- Description
Number of entries in your store.
- Name
numPages- Type
- int
- Description
Number of pages in your store, i.e. ceil of numEntries // pageSize.
- Name
pageSize- Type
- int
- Description
Maximum number of entries in this page.
The store entry model
The store entry contains information about the storeId, its data and the timestamp when it was created.
Properties
- Name
id- Type
- string
- Description
Unique identifier for the store entry.
- Name
storeId- Type
- string
- Description
Unique identifier for the store.
- Name
record- Type
- dict
- Description
The actual store entry data.
- Name
timestamp- Type
- timestamp
- Description
Timestamp of when the store entry was created.
Retrieve a store
This endpoint allows you to retrieve a store by providing their id. Refer to the list at the top of this page to see which properties are included with store objects.
Optional attributes
- Name
page- Type
- int
- Description
Which page to load from the store.
Request
curl https://app.kern.ai/workflow-api/stores/WAz8eIbvDR60rouK?page=1 \
-H "Authorization: {token}"
Response
{
"id": "1e844bf2-5ebb-40a5-8aa4-7e6b5e79479a",
"organizationId": "8502b0fb-cfaf-45ce-b0a7-71231cb8e769",
"name": "My store",
"integration":
"Workflow Read",
"description": "Reads data from an API or a UI",
"icon": "workflow",
"entries": [{
"id": "87e71284-4c3f-46a1-a58c-55ccc08c7349",
"storeId": "1e844bf2-5ebb-40a5-8aa4-7e6b5e79479a",
"record": {"field_1": "This is an example!"},
"timestamp": "2023-02-13T20:22:03.260008"
}, {
"id": "6e86b3ad-5436-4c23-bfb2-036216166c76",
"storeId": "1e844bf2-5ebb-40a5-8aa4-7e6b5e79479a",
"record": {"field_1": "Hello World"},
"timestamp": "2023-02-13T20:21:59.775006"
}],
"numEntries": 2,
"numPages": 1,
"pageSize": 25,
"configSetup": {
"config": {"field_1": "Text"}
},
"configActions": {},
"state": "RUNNING",
"refineryProjectId": "None"
}
Post an entry
This endpoint allows you to post entries to your store. Note: If the record doesn't fit the expected schema, the API will return a 400 status code.
Request
curl -X DELETE https://app.kern.ai/workflow-api/stores/WAz8eIbvDR60rouK/add-entry \
-H "Authorization: {token}"
Response
{
"id": "70ecd4ad-9270-43ea-b439-5ee628833016",
"storeId": "1e844bf2-5ebb-40a5-8aa4-7e6b5e79479a",
"record": {"field_1": "Text"},
"timestamp": "2023-02-13T20:25:57.822324"
}